科研动态Research News |我院特聘副研究员Neupane在国际TOP期刊Chemosphere发表学术论文
华南师范大学地理科学学院/学院新闻2022-10-31 13:23:41来源:华南师范大学评论:0点击:收藏本文
我院特聘副研究员Bigyan Neupane在国际TOP期刊Chemosphere杂志上发表学术论文
Bigyan Neupane, Distinguished Associate Researcher of School of Geography publishes academic paper in Chemosphere, a top international journal
最近,华南师范大学地理科学学院特聘副研究员Bigyan Neupane作为第一作者,在国际TOP期刊“Chemosphere”上发表了一篇题为“人为汞污染的历史和强度:中国东北多湖沉积物200年的记录”的科学论文(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136803) 。鲍锟山研究员是本文的通讯作者。
中国东北地区人类活动的大幅度扩张导致环境污染物排放量增加。湖泊沉积物中此类环境污染物的长期记录提供了参考基准,据此可以评估人为环境变化的性质、强度和历史规律。为此,地理科学学院的鲍锟山研究员及其合作者领导的团队对中国东北松嫩平原11个湖泊沉积物岩芯中的汞浓度、积累速率和潜在来源进行了综合分析。汞富集系数和地累积指数表明,这些湖泊普遍受到汞的中度污染。利用汞积累速率重建了汞的污染历史:从20世纪初开始,汞浓度呈上升趋势,同时人为排放量也有所增加,在20世纪50年代中期有所增加,从90年代后期开始略有下降。人为汞的增加趋势与中国的改革开放进程相吻合,而汞积累速率的变化特征与该地区生物质燃烧和化石燃料消耗量的变化历史一致。这些结果阐明了过去百年来东北地区人为污染的强度和历史规律,强调了确定汞源对减少汞排放和指导实施有效缓解汞污染战略的重要性。
本研究得到了国家自然科学基金(批准号:41991252和41971113)、科技部外国专家计划(编号:QN2022030007L)和华南师范大学青年拔尖人才科学研究基金(118/8S0593)的资助。
Chemosphere是环境科学和环境化学领域的知名期刊之一(Q1期刊),2021影响因子为8.943。
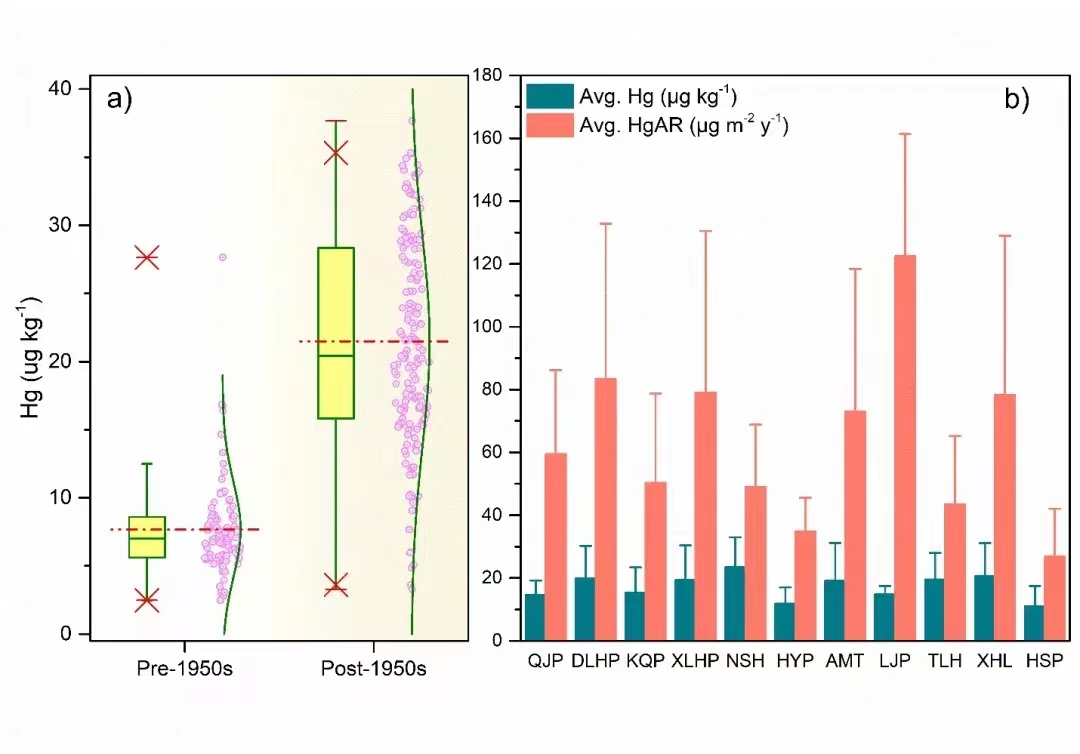
图1.a)20世纪50年代之前和之后(工业发展之前和之后)所有调查湖泊岩芯的汞浓度箱线图。红色虚线代表平均值,绿色水平线代表中间值,误差条代表数值的第5、25、75和95个百分位。绿色曲线代表正态分布;粉红色圆圈表示汞随时间的浓度;b)每个湖心的平均汞浓度和平均汞积累率。误差条表示标准偏差。
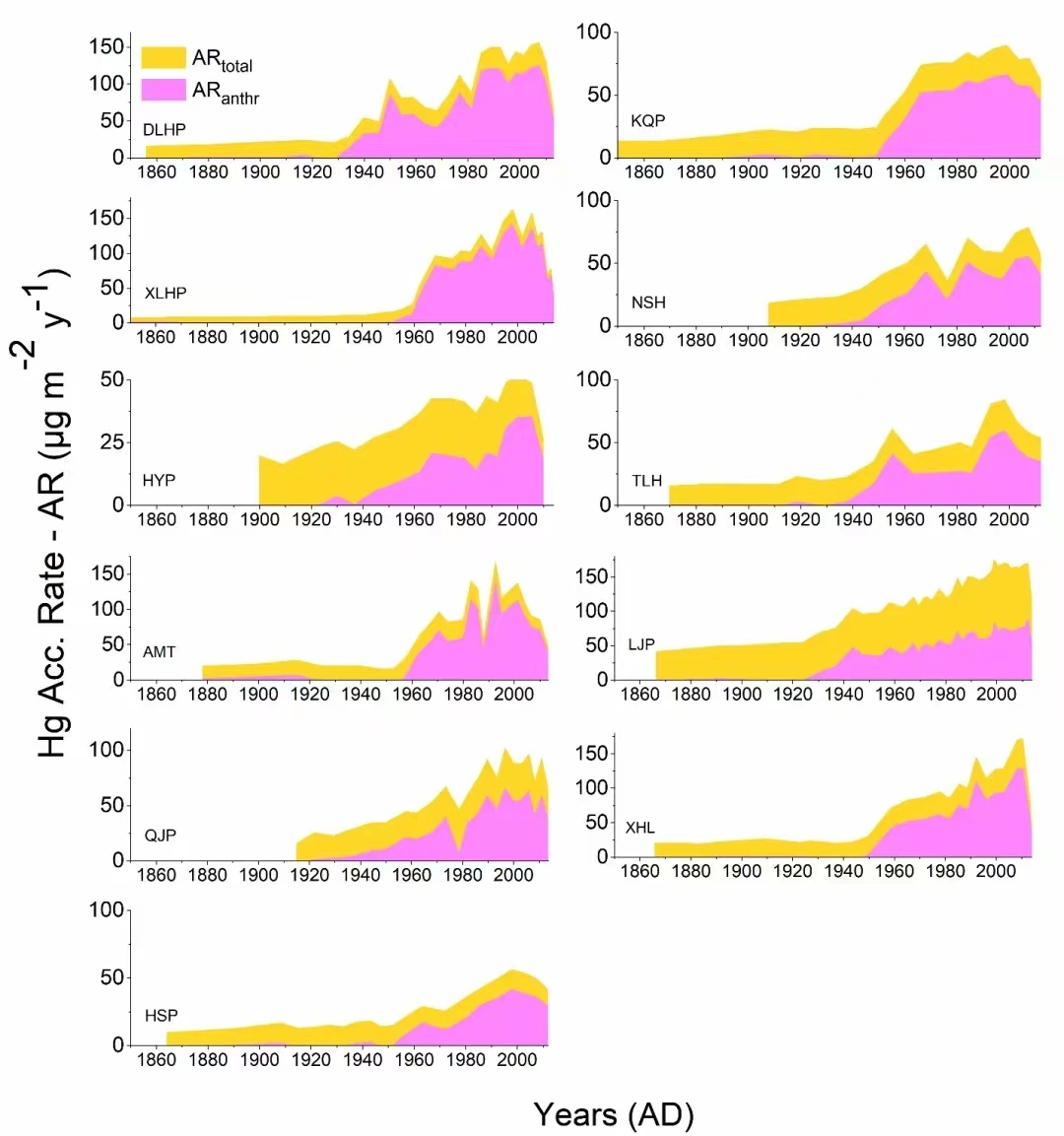
图2. 所有湖泊岩芯中总汞(ARtotal)和人为汞积累率(ARanth)的时间趋势
Recently, Bigyan Neupane, a Distinguished Associate Researcher at School of Geography, South China Normal University published a scientific paper titled “The timing and magnitude of anthropogenic mercury pollution: A 200-year record from multi-lake sediment cores in northeast China” as a first author in an international journal “Chemosphere”. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136803).
The recent substantial expansion of human activities in northeast China has resulted in increased emission of environmental pollutants. Longer-term records of such environmental pollutants provide a benchmark against which it is possible to evaluate the nature, extent and timing of anthropogenic environmental changes.
In response to this need, the team led by Kunshan Bao of the School of Geography and its collaborators, tested and analyzed the concentration, accumulation rate and sources of mercury (Hg) in 11 lake sediment cores from the Songnen Plain in northeast China. Based on this measurement, this study presented a reconstruction of the historical deposition of Hg as an indicator of the changing scale of human impact. The results demonstrate an increasing trend of Hg concentration, concurrent with elevated anthropogenic emissions, beginning from the early 1900s, accelerating through the mid-1950s and slightly decreasing from the late 1990s onwards. The increase in anthropogenic Hg coincides with the reform and opening up of China, which precipitated social and economic transformation, and rapid industrial and economic growth. Measurements of the Hg enrichment factor in all the cores enables identification of the anthropogenic contribution to Hg accumulation. The geoaccumulation index indicates that the lakes are in general moderately polluted by Hg. The historical trend of Hg accumulation rate parallels the temporal progression of biomass burning and fossil fuel consumption in the region. The findings elucidate the extent of anthropogenic pollution in the Anthropocene and underline the importance of identifying Hg sources to reduce emissions and guide the implementation of effective mitigation strategies.
Professor Kunshan Bao is corresponding author of the paper. This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 41991252 and 41971113), the Foreign Experts Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology (no. QN2022030007L) and Scientific Research Foundation for Young Talents of South China Normal University (118/ 8S0593).
Chemosphere is one of the leading journals in the field of environmental science and environmental chemistry (Q1 Journal) with a 2021 impact factor = 8.943.
文字编辑 | Bigyan Neupane
初审 | 袁亚娟
复审 | 陶伟
终审 | 刘云刚
标签: