科研动态Research News | 王琎特聘研究员在Giscience & Remote Sensing发表研究成果
华南师范大学地理科学学院/学院新闻2023-09-06 15:02:00来源:华南师范大学评论:0点击:收藏本文
王琎特聘研究员在Giscience & Remote Sensing发表研究成果
Wang Jin has published academic papers in Giscience & Remote Sensing
作者简介
王琎,华南师范大学特聘研究员。主要从事城市遥感、海岸带生态环境等研究,已发表SCI、中文核心及EI等论文近二十篇,其中第一或通讯作者十篇,近五年引用量200余次。参与编著生态学专著两部,并于2018年获全国地理信息科技进步二等奖。目前主持在研国家自然科学基金、广州市基础与应用基础研究等科研项目。
华南师范大学北斗研究院、地理科学学院王琎特聘研究员近日以通讯作者在地学与遥感领域主要期刊Giscience & Remote Sensing发表题为“Multitemporal impervious surface estimation via an optimized stable/change pixel detection approach”的研究论文(全文链接:https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15481603.2022.2118430),本研究从产生多时序复合误差的各关键因素出发,全面优化不透水面变化监测的技术流程,可以为城市环境的维持和保护提供基础数据与科学依据。
不透水面是衡量城市化进程和环境状况的重要指标。精确、高效的亚像元监测方法是城市遥感相关研究的基础,近年来受到高度关注。但在现有多时序监测研究中,亚像元方法自身系统误差和随机误差累积产生复合误差,往往导致监测结果在时间序列的一致性和分辨率等方面受到较大影响,难以准确反映地表变化的真实过程。本研究首先通过变化检测算法分析多时序遥感影像像元的变化特征,将研究区像元划分为变化像元和稳定像元;然后聚合所有的稳定像元及处于相对稳定期的变化像元,根据像元的变化情况重构多时序像元数据库;最后基于误差来源对现有亚像元方法进行耦合优化,并针对多时序像元数据库建模监测不透水面变化,进一步降低亚像元估测的误差,在国内外实验区均达到较高精度。与传统分类回归树方法相比,多时序优化后的平均绝对误差和均方根误差分别下降了15.55%和8.63%,相关系数达到0.96。此外,本研究提出的方法还显著降低了稳定像元多时序不透水密度的标准差。
Giscience & Remote Sensing重点关注遥感技术及其地学应用,最新影响因子为6.7,在地学、遥感领域均为JCR Q1期刊。
Recently, Research Professor Wang Jin of Beidou Research Institute, South China Normal University, published a research article entitled “Multitemporal impervious surface estimation via an optimized stable/change pixel detection approach” in Giscience & Remote Sensing as the corresponding author. This research comprehensively optimizes the technical process of impervious surface change monitoring from the perspective of various key factors that generate multi-temporal compounded errors, which can provide data source and scientific basis for the manage and protection of urban environment.
Impervious surface is an important indicator to measure the process of urbanization and environmental condition. However, systematic and random errors in the existing methods still impact the reliability of subpixel impervious surface estimation, generating compounded errors when conducting multitemporal monitoring. Two experimental areas located in Rome in Italy and Shenzhen in China were chosen to testify the generality of the proposed method to estimate different types of impervious surfaces worldwide. By reducing the compounded errors, the proposed method demonstrated its efficiency in achieving higher accuracy in both study areas without involving extensive data sources and intensive manual tasks. Compared with the conventional classification and regression tree algorithm, the overall mean average error and root mean square error of this study declined by more than 15.55% and 8.63%, respectively, and R2 increased from approximately 0.93 to 0.96. The proposed method also drastically reduced the standard deviation of the multitemporal percent ISA of the stable pixels.
Giscience & Remote Sensing is a Q1 journal in both geography and remote sensing categories with the latest impact factor of 6.4. It focuses on geographic information systems (GIS), remote sensing of the environment (including digital image processing), geocomputation, spatial data mining, and geographic environmental modelling.

图1 深圳市福田核心区亚像元不透水面变化(2013 - 2021)的多时序优化结果
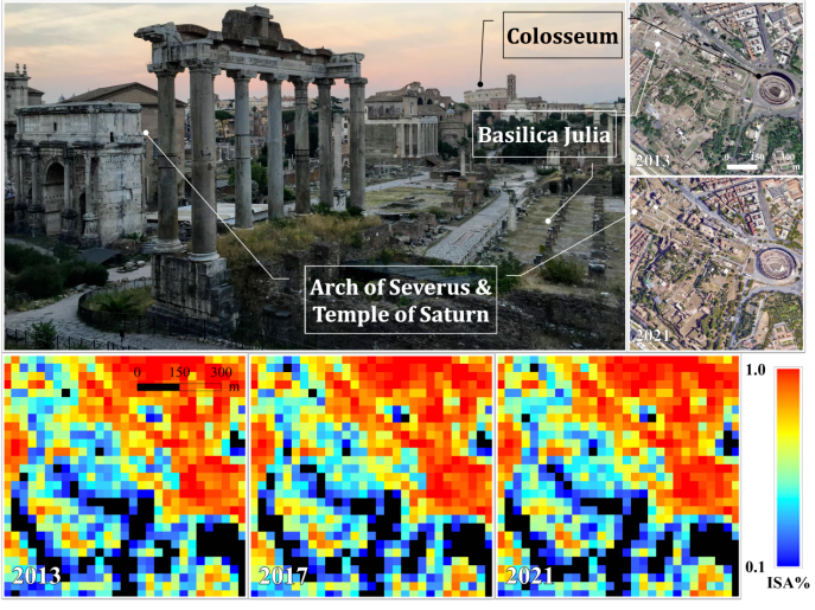

图2 古罗马广场及罗马大竞技场区域稳定像元的多时序亚像元不透水地图(2013 - 2021)
文案 | 王 琎
初审 | 袁亚娟
复审 | 陶 伟
终审 | 刘云刚
标签: