科研动态Research News | 王琎特聘研究员在Ecological Indicators发表研究成果
华南师范大学地理科学学院/学院新闻2023-09-06 15:10:00来源:华南师范大学评论:0点击:收藏本文
王琎特聘研究员在Ecological Indicators发表研究成果
Wang Jin has published academic papers in Ecological Indicators Sensing
作者简介
王琎,华南师范大学特聘研究员。主要从事城市遥感、海岸带生态环境等研究,已发表SCI、中文核心及EI等论文近二十篇,其中第一或通讯作者十篇,近五年引用量200余次。参与编著生态学专著两部,并于2018年获全国地理信息科技进步二等奖。目前主持在研国家自然科学基金、广州市基础与应用基础研究等科研项目。
近日,华南师范大学北斗研究院、地理科学学院王琎特聘研究员以第一作者在环境科学领域SCI Q1期刊Ecological Indicators发表题为“Continuous remote sensing ecological index (CRSEI): A novel approach for multitemporal monitoring of eco-environmental changes on large scale”的研究论文,中科院先进技术研究院陈劲松研究员为本文共同通讯作者(全文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470160X23008816)。本研究针对现有遥感方法在进行多时序生态环境质量评价时存在的不稳定偏差问题,提出并构建了一种改进的遥感指数——连续遥感生态指数(CRSEI),适用于在大空间尺度、高时间分辨率下定量评价生态环境质量,可以准确反映地表环境的复杂变化。该研究为生态环境监测提供了一种新的遥感指标和方法,并为沿海地区的环境保护和可持续发展提供了科学依据。
本研究以东亚和东南亚的沿海地区为例,利用2001-2019年的MODIS数据计算了CRSEI,并对其中各区域的生态环境质量变化进行了对比分析。研究结果表明,CRSEI能够连续地反映生态环境质量的真实变化,并提供在时序上可比的定量评价结果。二十年间,研究区的CRSEI总体略有下降,但各区域表现出不同的变化趋势。其中,中国北部沿海地区虽然生态环境质量相对较低,但取得了最大的改善幅度;而越南和柬埔寨沿海地区的生态环境显著恶化,主要原因是人类活动导致的热带雨林破坏。此外,本研究还发现区域生态环境质量与人口密度的变化高度相关。
Ecological Indicators重点关注生态环境的定量分析研究,是该领域top期刊(最新中科院分区),最新影响因子6.9。
Recently, Research Professor Wang Jin from the Beidou Research Institute and School of Geography Science at South China Normal University published a research paper titled "Continuous Remote Sensing Ecological Index (CRSEI): A Novel Approach for Multitemporal Monitoring of Eco-Environmental Changes on Large Scale" as the first author in the SCI Q1 journal Ecological Indicators in the field of Environmental Science (full article link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470160X23008816). This study addresses the issue of unstable bias in existing remote sensing methods for multitemporal eco-environmental quality assessment. The researchers proposed and constructed an improved remote sensing index called the Continuous Remote Sensing Ecological Index (CRSEI), which enables quantitative evaluation of eco-environmental quality at a large spatial scale and high temporal resolution, accurately depicting complex changes in the earth's surface environment. This research provides a new remote sensing index and method for ecological environment monitoring and offers scientific references for environmental protection and sustainable development in coastal areas.
In this study, the coastal regions of East and Southeast Asia were taken as examples, and MODIS data from 2001 to 2019 were used to calculate the CRSEI and analyze the changes in eco-environmental quality in different regions. The results demonstrate that CRSEI can continuously reflect the spatiotemporal changes in eco-environmental quality and provide comparable quantitative evaluation results over time. Over the twenty-year period, the overall CRSEI of the study area slightly decreased, but the subregions showed different change trends. Notably, the coastal areas in northern China experienced the greatest improvement in eco-environmental quality, while the coastal areas of Vietnam and Cambodia witnessed significant degradation due to tropical rainforest destruction caused by human activities. Additionally, the study found a significant correlation between the changes in regional eco-environmental quality and population density.
Ecological Indicators is a leading journal that focuses on quantitative analysis of ecological environments, and it is rated as a top journal in the field (latest Chinese Academy of Sciences category) with a recent IF of 6.9.
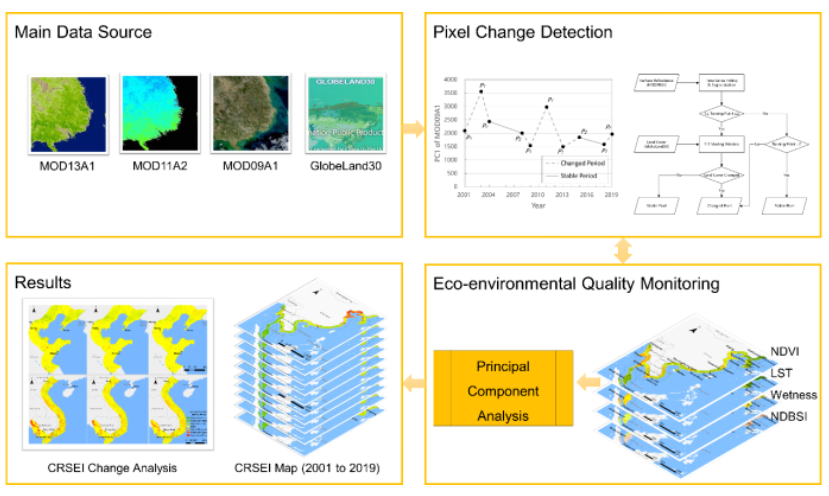
图1 本文研究架构图
文案编辑 | 王 琎
初审 | 袁亚娟
复审 | 陶 伟
终审 | 刘云刚
标签: